When someone leaves your organization, it is essential that all their information is removed from the official network and kept in retention. Additionally, you must also restrict their access for security reasons. So, in this blog, I will provide the best practices for retaining mailboxes in Microsoft 365.
When removing users in Office 365, you must apply a retention hold on their emails to create an archive. To do that, go into the Exchange admin center and select the mailbox for which a retention hold is required. Once you set a retention hold on emails, you can use the eDiscovery section in Compliance to access the archive information.
- The best way to set a retention hold on deleted mailboxes.
- How to view the mailbox achieved even after a user leaves an organization.
Please continue reading for an in-depth guide on retaining mailboxes in Microsoft 365.
The best way to set a retention hold on deleted mailboxes
The best way to archive mailbox information is to set a retention hold for email mailboxes. For this, you need to go into the Exchange mailbox service and then go to the mailbox and set retention from there. Microsoft will automatically hold this information with a retention policy. When you set a policy, you can delete the user mailbox from the official network, and Microsoft will hold the user information.
Microsoft keeps mailbox information for 30 days as a default before the mailbox information goes from the network. Setting a retention policy will allow you to extend the date to unlimited. This is why it is better to manually set up a retention policy than rely on the automated retention system, which will only hold the information for 30 days.
- Firstly, open Office 365.
You will need admin permissions to proceed with the steps ahead.
- Now click on the launcher illustrated by nine dots.
Nine dots represent the launcher in Office 365. On the top left-hand side of the display, click on this to view the list of applications.
- Click on the option for “Admin.”

- Under the list of Admin centers, click on “Exchange.”
- Under recipients, click on “Mailboxes.”

- Double-click on one of your mailboxes.
- From the new panel that has opened, click on “Others.”
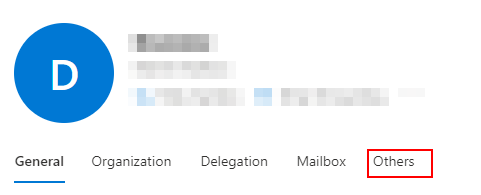
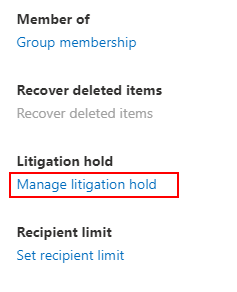
- Under litigation hold, click on “Manage litigation hold.”
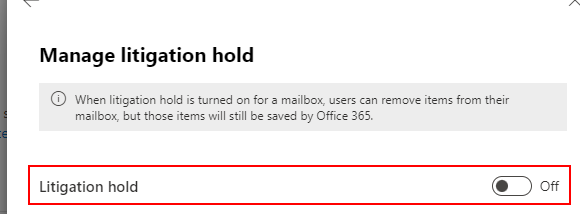
- Turn “Litigation hold” on.
- Fill out the retention policy information.
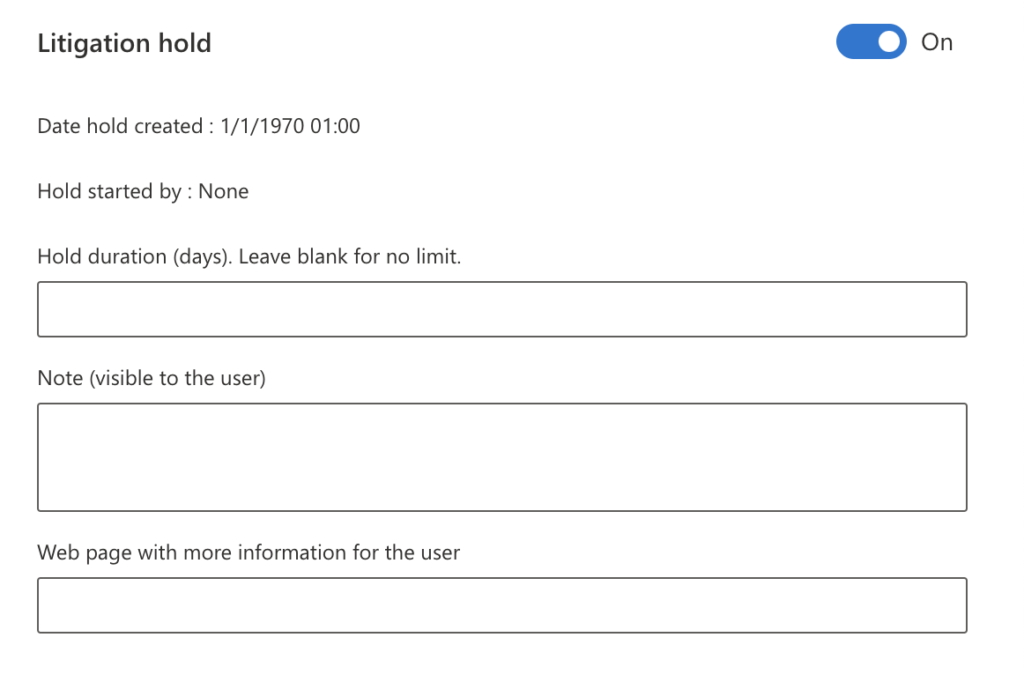
- Click on “Save” to complete the process.
You can delete a user’s Microsoft 365 account if they leave your company (or take a long leave of absence). After you delete the employee’s account, the mailbox information is retained for 30 days. You can still restore the mailbox data throughout this time by restoring the account.
However, the mailbox will become inactive if you place a hold before the Microsoft 365 account deletion. The holds you may use with Microsoft 365 retention and eDiscovery holds are discussed in the section above.
When your company wants to save the contents of former workers’ emails for legal, regulatory, or other reasons, inactive mailboxes might be handy. We advise implementing a Microsoft 365 retention policy or labels, verifying the hold is applied and removing the relevant Microsoft 365 account.

How to view the mailbox achieved even after a user leaves an organization.
Microsoft has created a section in Compliance manager where you can view email archives. If you have used the method above and applied a retention policy on one of your mailboxes for a user leaving the organization, you can use the Compliance section to view the email archives.
- Firstly, open Office 365.

- Click on the launcher and then click on “Admin.”

- From the list of admin centers, click on “Compliance.”
- Scroll down and click on the drop-down next to “eDiscovery.”

- Click on “User data search.”

- Click on “Create a case.”
- Input a name for your case and some description.

- Click on the option for “Next.”

- Now select the mailbox in question.
- Then click on “Next.”

- Now click on “Save.”

- A new window will open, and you can view the mailbox archives here.
The process may take some time to load as there may be quite a few emails inside the archive. However, once this section has loaded, you can view a full list of the email archives from the retention hold. Remember that it will only display information from when you set the retention hold in the Exchange center.
Microsoft will keep this information for as long as the time you set in the retention hold. I did not set a time in my example, meaning the system will hold the contents until further notice.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our content on the best practices for retaining mailbox information after a user leaves an organization. I provided the list of steps you can use to help create retention for the mailbox. I have also provided the steps and how you can use the eDiscovery section to view archive mailboxes.
A retention hold doesn’t have a time limit, so you can set the policy as long as you want. A default policy set by Microsoft is only 30 days. After this time, the information is deleted without any notice. If you encounter any issues when trying to follow the steps, drop a comment below, and I will address them.
