Is your internet connection suitable for VoIP? To figure that out, you need to know whether VoIP uses upload or download.
Does VoIP use upload or download? VoIP uses upload and download. VoIP uses approximately 100Kbps upload and download bandwidth per call.
Depending on the way you deploy VoIP, your system could require a greater amount of bandwidth per call. Let’s explore what affects how much bandwidth your VoIP calls require.
How Much Upload and Download Speed Do I Need For VoIP?
The majority of the time, you will need 100Kbps upstream and downstream of dedicated bandwidth per VoIP phone call. However, requirements can differ due to numerous factors.
The dedicated bandwidth that you need for VoIP depends primarily upon the number of calls you will be making at any given time and the codec that your system uses.
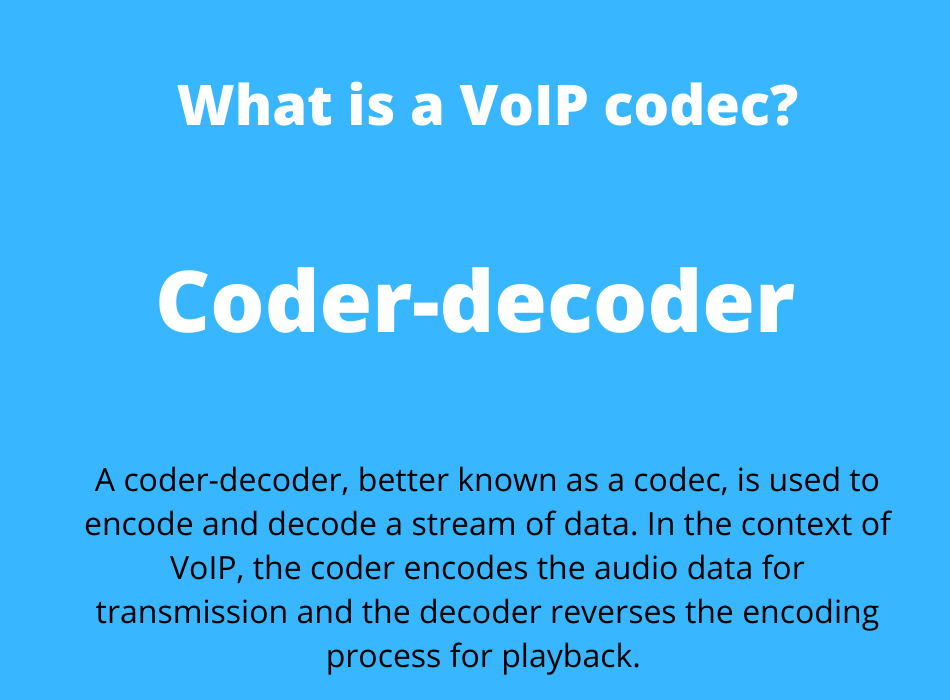
Codecs are really important for VoIP. A codec used for VoIP determines the sound quality of the call.
The word codec is a blend of the phrase coder-decoder. The coder encodes the data for transmission, whereas the decoder reverses the encoding process once the data reaches its destination.
All VoIP systems use a codec to transmit voice data, as the transmission would require too much bandwidth without compression. Furthermore, quality would be difficult to ensure if codecs were not used to compress data into a size requiring less bandwidth to transmit.
The codec you use will have a big impact on the bandwidth required per call. Some codecs will offer high voice quality but require a lot of bandwidth. Similarly, some codecs will offer lower voice quality but also require less bandwidth per concurrent call.
Codecs Commonly Used For VoIP
| Codec | Bandwidth Needed |
|---|---|
| G.711 | 100Kbps |
| G.722 | 64Kbps |
| G.723.1 | 6.3Kbps |
| iLBC | 15Kbps |
| Silk | 6 - 40Kbps |
| G.729 | 40Kbps |
The table above lists several of the codecs that are widely used for VoIP. Some are used by applications. For example, SILK was designed by Skype Limited to be used with Skype. Others are more widely used in commercial voice over IP telephone systems. For example, the G.711.
You have to be careful when choosing a codec. Choose the wrong one and your telephone system might cause your business a lot of problems. Here are some questions to ponder when choosing a codec for your system:
- What type of data connection do you have?
- How much bandwidth is available to dedicate to VoIP calls?
- How many calls will you be making at any one time?
- Are there any ‘spikes’ during the year where you would be making and receiving more calls?
The answers to these questions will help you to determine which codec is the best for your business telephone system.
To work out how much bandwidth you will need for your VoIP system, decide on a codec and then multiply the bandwidth required number by the number of concurrent calls you anticipate. For instance, if you choose the G.711 codec and you will be making 10 calls at any given time, you will need 1Mbps downstream and upstream of dedicated bandwidth at all times (100Kbps multiplied by 10).
So we’ve covered how much bandwidth is needed for VoIP. The next question I hear is always “what happens when I don’t have enough bandwidth available?”

What Happens When There Isn’t Enough Bandwidth For Calls?
Let’s explore a hypothetical scenario where your data connection is at its limit and another one of your users tries to make or receive a phone call. What happens?
According to numerous SME and enterprise VoIP providers, as soon as you get to the point of exceeding the available bandwidth, everything grinds to a halt. It won’t just affect the user that is making or receiving a call; it will affect every user.
At best, it can cause a bit of jittering. At worst, it can cause calls to drop. Data packets will not transfer properly, which means conversations can be garbled and incomprehensible. Moreover, it will also affect your business processes beyond VoIP. For example, users trying to access your CRM might struggle, because the bandwidth isn’t available.
Providers will explain that it’s important to make sure you have enough bandwidth, but they might not explain why. No provider wants to admit that their service might not work perfectly! Now you know what can happen if you don’t have enough bandwidth, you must endeavour to ensure that you do.
It’s evident that you must make sure you have enough bandwidth for VoIP. Next, I’ll offer some advice on how to guarantee your system operates as it should.
How To Make Sure You Have Enough Bandwidth For VoIP
VoIP doesn’t require a tonne of bandwidth, but it’s important to make sure you have enough. It’s worth noting that VoIP requires good download and upload speeds. Some connections offer suitable download speeds, such as fibre to the cabinet, but may not have upstream bandwidth. This can create a bottleneck, causing calls to fail and reducing call quality.
So how can you make sure that you always have enough bandwidth for VoIP?
Install a connection solely for voice over IP
Want to ensure you always have enough bandwidth for VoIP? One of the methods providers often deploy is installing a data connection solely for your voice over IP telephone system.
A second connection is one of the most viable ways to ensure you always have enough bandwidth for VoIP calls.
Some might see this as a ploy by providers, intended to make your business spend more money than it needs to. However, installing a second connection is one of the most viable ways to ensure you always have enough bandwidth for VoIP calls.
Depending on the size of your business and the number of calls you’ll be making concurrently, one data connection might not suffice. If you think that you can get by on one broadband connection, consider all the other processes consuming bandwidth in your building. If your business relies on its data service for a lot of critical processes, installing a connection solely for VoIP is often necessary to ensure call quality isn’t affected by other ongoing processes.
Configure your network to prioritise voice over data
If you cannot afford the expense of a connection to be used only for your telephone system, there are other ways to ensure high voice quality when using VoIP. For instance, you can configure your network to prioritise voice over data, thereby ensuring your voice calls are high quality.
Usually voice prioritisation will take place at router-level. Most business-grade routers will have a feature that enables voice traffic to be prioritised over any other type of traffic. This feature, as the name suggests, will ensure voice traffic is always transmitted before anything else. Essentially, it means VoIP gets its share of the bandwidth before any other process does.
Usually your internet service provider can configure your router to ensure voice traffic is prioritised. If you have an IT team, they should be able to do it for you too.
Use a codec that requires less bandwidth
This brings us back to the topic of this blog post: codecs. If you’re struggling for bandwidth, one of the easiest ways to ensure you always have enough capacity for VoIP is use a different codec!
As I’ve already covered in this blog post, different codecs require a different amount of bandwidth. If you are using the G.711 codec, for example, it will require more than double the dedicated bandwidth needed by the G.729 codec.
If you find that the quality of your VoIP calls is poor due to jittering and dropping, it may suggest that you’re struggling for bandwidth. If you’re facing this problem, try changing over to a codec that requires less bandwidth.
