A shared mailbox is one that may be used by numerous individuals to read and send email messages. A shared mailbox is a sort of user mailbox that does not have its own username and password. It can also be used to provide a single calendar, allowing several users to arrange and view vacation time or work shifts. As a result, users are unable to access them directly. You can allow other people to receive and respond to email messages and meeting requests sent to an Office 365 shared mailbox if you’re the administrator of the mailbox. You decide on their level of access. You can give them access to read items in the mailbox as well as create, modify, and remove items. Follow the steps below to see how.
How to give read-only access to a shared mailbox in Outlook (Microsoft 365):
- Sign into
 Office 365 and navigate to Outlook
Office 365 and navigate to Outlook - Login to an Outlook account that has full access permissions to a shared mailbox.
- Visit the profile by clicking on the profile picture.
- Click on “open another mailbox”.
- Right-click the shared mailbox’s primary folder, then choose permissions.
- As seen in the image below, add the user to the box and then grant reviewer authority to the user.
Shared mailboxes allow a group of individuals in your organization to easily monitor and send email from a single account, such as [email protected] or [email protected]. When a group member answers to an email sent to the shared mailbox, the email seems to have been sent by the shared mailbox rather than by the individual user.
We’ve also created a video to help guide you through the steps:
Shared Mailbox permissions for Outlook in Microsoft 365 to give read-only access
Send on Behalf:
- The Send on Behalf ability allows a user to send email on behalf of a shared mailbox. If user one enters into the shared mailbox and sends an email, the message seems to have been sent “on behalf of the Mailbox.” You must use a Set-Mailbox instead of the EAC to give Send on Behalf rights.
Send As:
- When sending mail, the Send As permission allows a user to mimic the shared mailbox. If user 1 logs into the shared mailbox Marketing Department and sends an email, it will appear that the email was sent by the Marketing Department.
Full Access:
- This permission allows a user to open a shared mailbox and behave as the mailbox’s owner. A user can add calendar items, read, view, delete, and edit email messages, and create tasks and calendar contacts after gaining access to the shared mailbox. However, unless they also have Send As or Send on Behalf access, a user with Full Access can’t send email from the shared mailbox.
Note that Users will really send as the mailbox owner if full access rights and Send on Behalf permissions are provided to a mailbox. Full access rights allow a user to sign in to a mailbox using Outlook or Outlook Web Access and then add that mailbox to Outlook as a secondary mailbox. Full access rights, on the other hand, prevent the user from sending as or on behalf of the mailbox. Those permits are given on a case-by-case basis.
Only when adding a delegate via Outlook may end users grant send on behalf. Delegates can be given folder rights, receive meeting invitations, and have sent on Behalf permissions for the mailbox. Users can set delegates in Outlook only for their own mailboxes starting with Exchange 2010. Users are unable to assign delegates to shared mailboxes.
Outlook permission categories in Microsoft 365
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Owner | All objects and files may be created, read, modified, and deleted, as well as subfolders. You can alter the permission levels that other users have for the folder as the folder owner. (Note that this does not apply to delegates.) |
| Publishing editor | All documents and files may be created, read, modified, and deleted, as well as subfolders. (Note that this does not apply to delegates.) |
| Editor | All things and files may be created, read, modified, and deleted. |
| Publishing Author | Create and read things and files, as well as subfolders, as well as change and remove items and files. (Note that this does not apply to delegates.) |
| Author | Create, read, and change things and files, as well as remove items and files you’ve created. |
| Nonediting Author | Non-editing Authors can create and read files, but can’t modify or delete them. |
| Reviewer | Only read objects and files. |
| Contributor | Only create objects and files. The folder’s contents do not appear. (Note that this does not apply to delegates.) |
| None | You do not have authorization. You are unable to open the folder. |
| Custom | Carry out the tasks specified by the folder’s owner. (Note that this does not apply to delegates.) |
Licenses: You can keep up to 50GB of data in your shared mailbox without assigning it a license. After that, you’ll need to give the mailbox a license so it can hold more data. Please visit Exchange Online Limits for additional information on shared mailbox licensing. You’ll be able to receive an email for a while after a shared mailbox exceeds its storage limit, but you won’t be able to send a new email. After then, it will cease to receive email. A non-delivery receipt will be sent to those who send mail to the mailbox.
Use with Outlook: You can access shared mailboxes using the ![]() Outlook for iOS or Android apps, in addition to using Outlook on the web from your browser.
Outlook for iOS or Android apps, in addition to using Outlook on the web from your browser.

How to give read only access to a shared mailbox in Outlook (Microsoft 365)
Step by step Breakdown:
- First,
 Sign into Microsoft 365 and open Outlook.
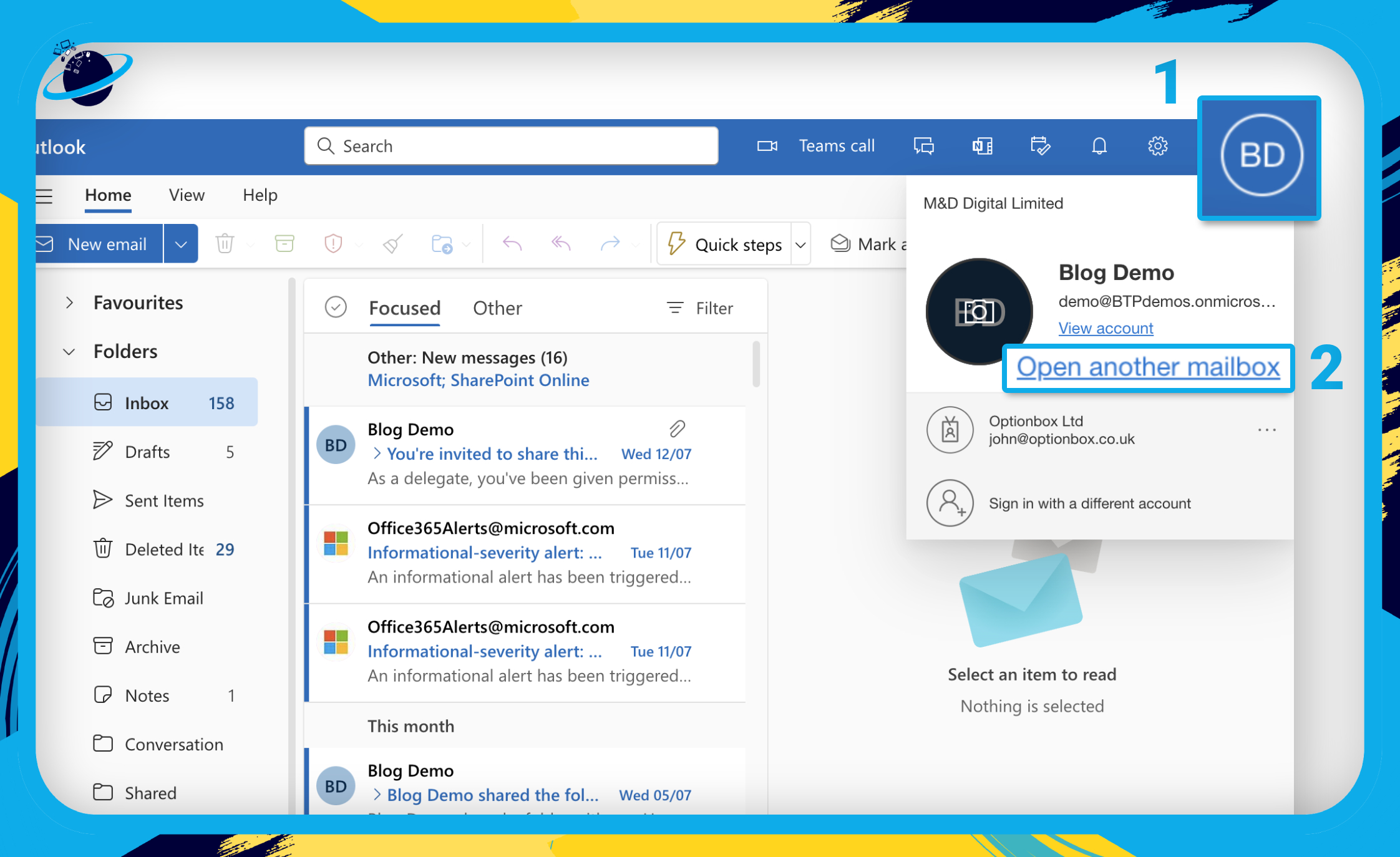
Sign into Microsoft 365 and open Outlook. - Click your profile image in the top right. [1]
- Then select “Open another mailbox” from the dropdown. [2]
- Now right-click the shared mailbox’s “Inbox” folder. [1]
- Select “Sharing and permissions” from the popup menu. [2]

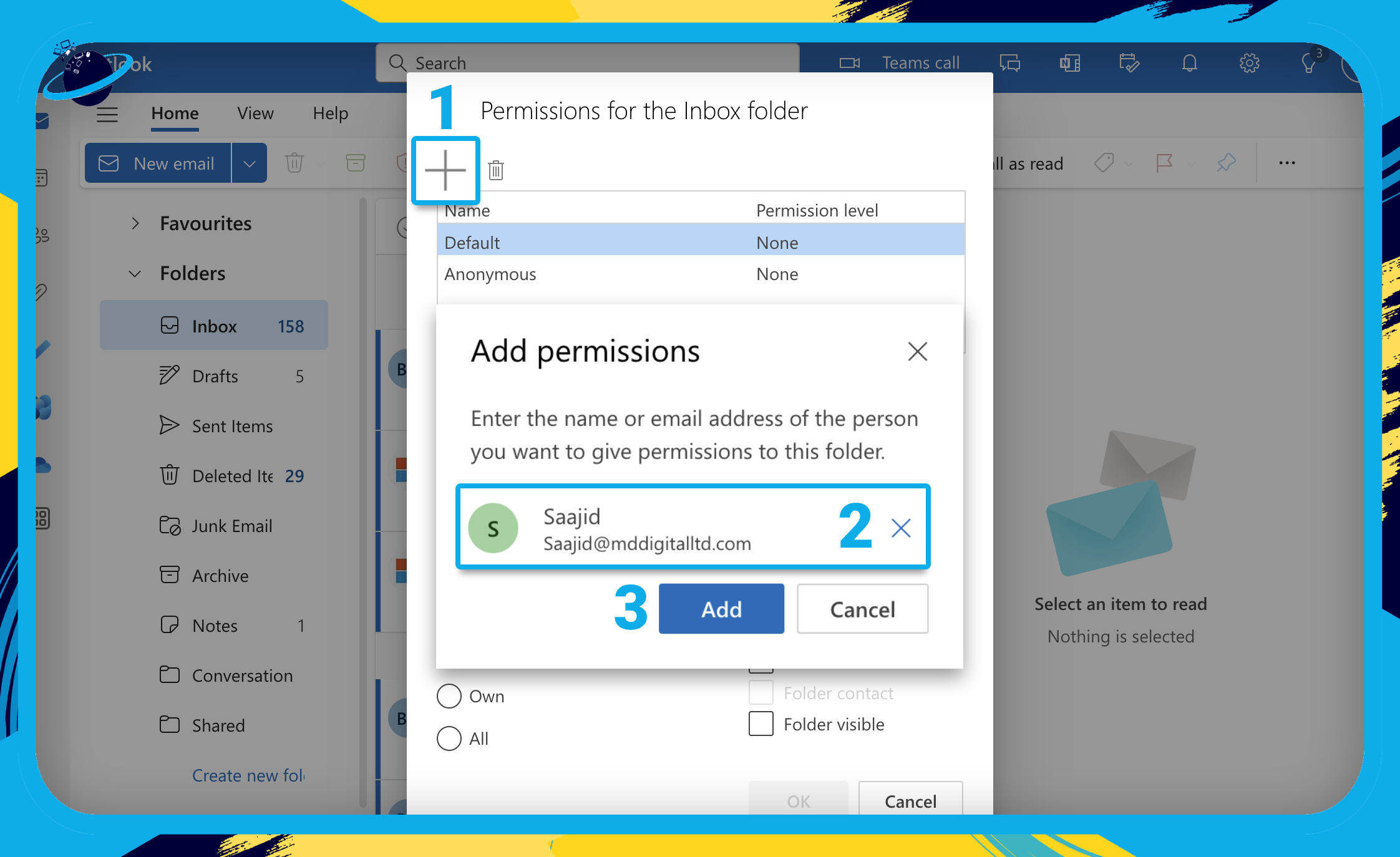
- Click the plus icon in the top left of the permissions dialog box. [1]
- Enter and select the name of whoever you want to add. [2]
- Click the “Add” button. [3]
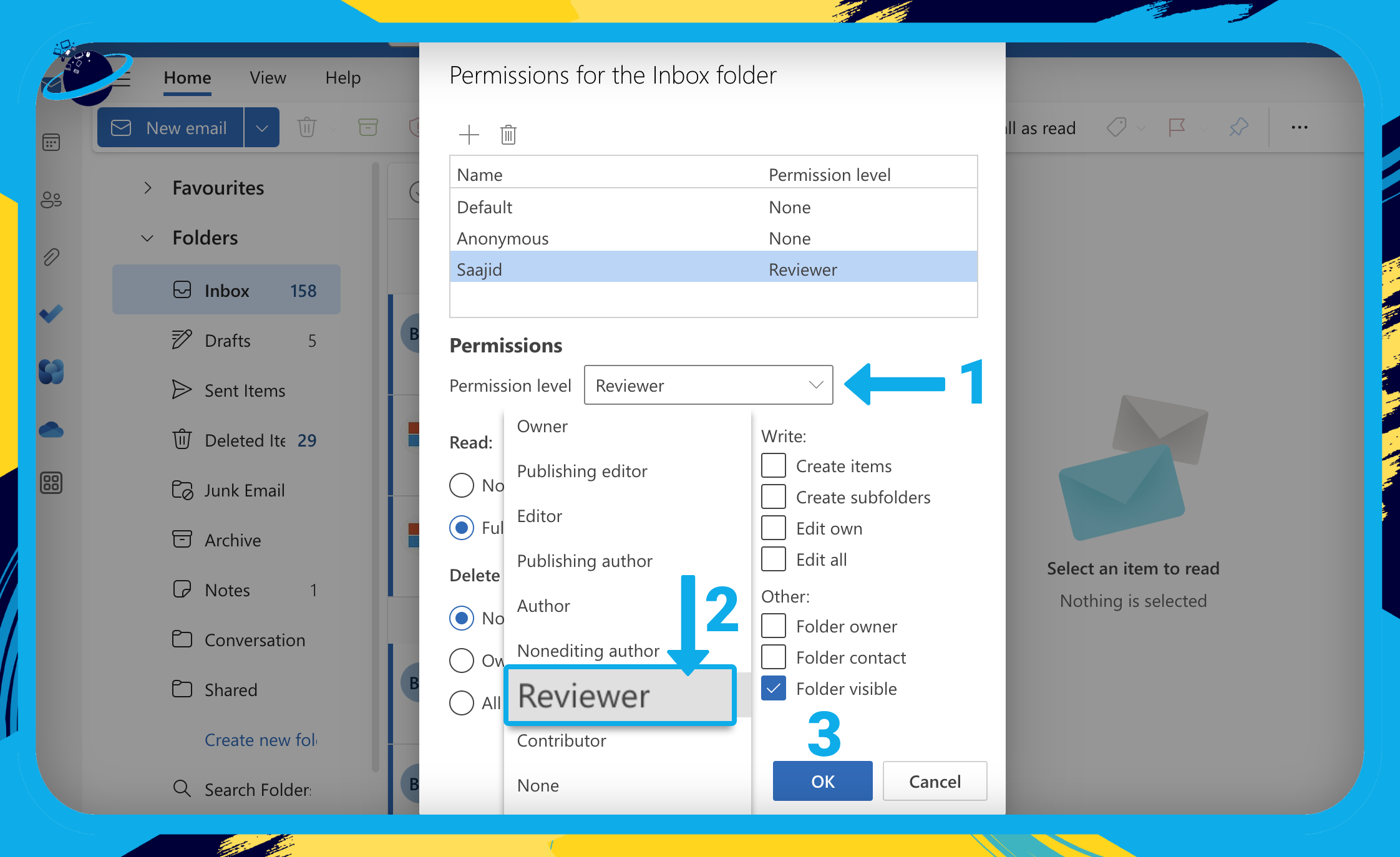
- Click the select box next to “Permission level.” [1]
- Select “Reviewer” from the dropdown. [2]
- Finally, hit “OK.” [3]
Conclusion
In conclusion, a shared mailbox in Outlook (Microsoft 365) offers a convenient way for multiple users to access and manage email messages collectively. By following a few simple steps, you can grant read-only access to a shared mailbox, allowing others to view and respond to emails and meeting requests. This level of access can be customized based on individual needs and responsibilities within your organization.
Additionally, permissions such as “Send on Behalf,” “Send As,” and “Full Access” provide further flexibility in managing shared mailboxes. It’s important to note that these permissions are granted on a case-by-case basis, ensuring proper control and security.
Shared mailboxes enhance collaboration and streamline communication, making them an invaluable tool for efficient teamwork. So, give your team the advantage of a shared mailbox in Outlook and simplify your email management process.
Thank you for reading!